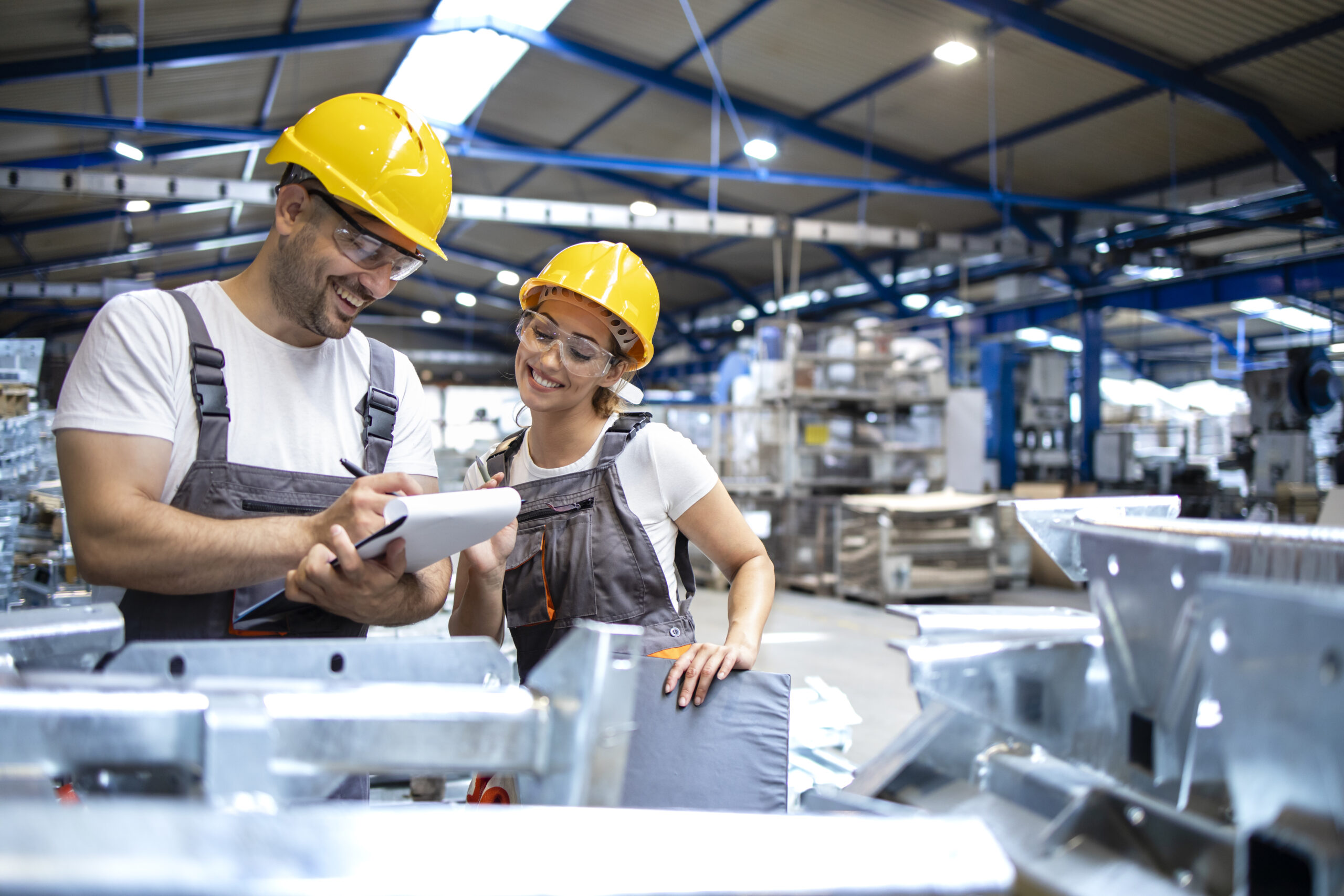
Organizations keep track of and manage the products they purchase, store, dispense, and use through inventory management. The components or raw materials used to create products are considered “goods” by some businesses, such as manufacturers. It is stock that is prepared for sale for others, such as merchants.
Diverse businesses have different inventory management requirements and strategies. The goal, however, is always the same: Provide the proper quantity of items at the proper time and location, regardless of the business or industry.
Using Warehouse Inventory Management and Assisted Field Service together
Combining Guided Field Service and Warehouse Inventory Management Inventory can be tracked throughout its lifecycle with guided field service. These are some ways that field service can help to improve warehouse inventory management.
- Management of Stocks
For any site where you keep your inventory, such as a warehouse, you can build a field service location. It is now simpler to keep track of your stock and to plan for renewal before the stock runs out.
- Follow Service Providers
Products can be added to work orders, job types, and work order line items. You might trace your orders and service providers more easily as a result.
- Monitor Inventory Consumption
You can create line items for the goods and materials that will be used in production by using guided field service. This will enable you to constantly monitor the usage of the products in your inventory.
- Control the Transfer of Commodities
The movement of items between your corporate warehouse and various storage locations may be simply tracked and managed. To keep track of pertinent transportation-related information, you can construct shipments.
Best techniques for inventory management
To follow best practises for inventory management, you must understand how much to order, how long it takes for your supply to run out, when to place new orders, and how much to maintain on hand. Costs associated with shipping and storage must also be considered.
These fundamental ideas are constant throughout all industries. The best practises for inventory management, however, varied significantly depending on the requirements of businesses in different industries.
How to Avoid the Pitfalls of Inventory Optimization
- Interrupted post-purchase trips
To provide a seamless customer experience, an effective order management system (OMS) may integrate the underlying business, fulfilment, and service activities.
An increasing number of companies are also understanding that having a single source of truth for all orders and data enables them to provide a better customer experience, which raises customer happiness. 79% of consumers believe that an organization’s experiences are just as crucial as its goods and services.
- Overselling or underselling of stock
It will be less risky to oversell or undersell things if there is a system in place that can give real-time, location-level availability, particularly during high-volume periods like holidays or flash sales.
Customers would prefer receive a notification when an item they desire is back in stock than make an order for something that isn’t genuinely available.
- Failure to optimize fulfilment procedures
Businesses who operate several physical locations as well as distribution hubs in addition to their online shop sometimes struggle to maximize last-mile delivery.
Ensure that your OMS is adaptable enough to match your business’s evolving demands to address this issue. Provide dynamic routing options to enable simple order routing to the most suitable place for fulfilment. based on proximity and price, preventing split shipments.
Handle Inventories
- Establish field service locations for sites where your inventory is kept, such warehouses, so you can keep track of everything and prevent stockouts.
- Create product items after configuring your inventory settings, including page layouts and user permissions, to keep track of where your inventory is kept.
- For your service provider to keep track of the necessary components, add needed products to work types, work orders, and work order line items.
- To keep track of the usage or consumption of the things in your inventory, create line items for products that will be consumed.
- When your stock runs out, you’ll need to make a new product request and link it to the related orders, line items, locations, and accounts.
- To trace the transfer from one storage site to another to fulfil a new product order, you must construct a product transfer item.
Benefits of Inventory Management
- Improved Inventory Accuracy – Good inventory management allows you to order only the quantity of goods required to satisfy demand since you are aware of what is currently in stock.
- Inventory management makes it easier to keep track of what is in stock and what is backordered, lowering the risk of overselling.
- Stock incurs costs up until it is sold, saving you money. Transportation, processing, and storage expenses, as well as personnel wages, are all considered carrying costs.
- Staying away from Stockouts and Extra Stock – If an item is out of stock, the number of days it is out of stock is reduced and excess inventory is avoided thanks to better planning and management.
- Further insights – You may also quickly identify sales patterns using inventory management and stock control, as well as track recalled goods and expiration dates.
- Improved Agreements with Suppliers and Vendors – Understanding which items sell and in what quantities is another benefit of inventory management. Take use of such information to pressure suppliers into offering you better terms and rates.
- Increases in productivity – Solutions for effective inventory management free up time that could be used for other purposes.



